Liver transplant for cirrhosis is a life-saving option for those suffering from severe liver damage due to cirrhosis. As a condition that affects millions globally, cirrhosis can lead to significant complications, including liver failure. When the liver can no longer function properly, a liver transplant for cirrhosis may be the only viable solution. This article explores the importance of liver transplants, the process involved, and how they offer a second chance at life for individuals battling advanced cirrhosis.
Definition of Cirrhosis of the Liver
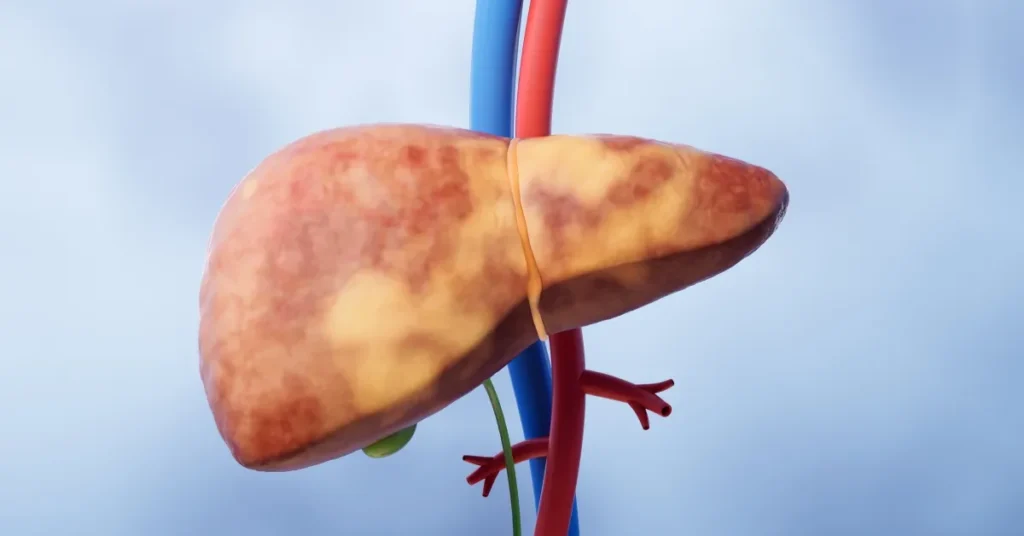
Cirrhosis is a chronic, progressive liver disease where healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue. Over time, this scarring disrupts the liver’s ability to function properly, leading to serious complications. Liver transplant for cirrhosis becomes a critical option when the liver’s function declines to a point where it can no longer perform its essential duties.
The liver plays a vital role in detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, and regulating essential metabolic functions. When scar tissue builds up due to cirrhosis, these processes are disrupted, leading to a decline in overall health.
Cirrhosis can be caused by several factors, including:
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Hepatitis B or C infections
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Autoimmune liver diseases
As the condition progresses, patients may experience symptoms such as jaundice, fatigue, and swelling in the abdomen. If left untreated, cirrhosis can lead to liver failure, making a liver transplant for cirrhosis the only life-saving option.
Partial liver transplant for cirrhosis may also be considered for some patients, allowing them to receive a portion of a healthy liver from a living donor. This procedure offers hope to those in need of a transplant but facing long waiting lists for a full liver.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis of the Liver
Symptoms of cirrhosis include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), swollen legs and abdomen, nausea, and unexplained weight loss. As the disease progresses, patients may experience confusion, easy bruising, and bleeding due to decreased liver function.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Swollen legs and abdomen (edema and ascites).
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
- Easy bruising and bleeding.
- Confusion and memory problems due to the buildup of toxins in the blood.
- Itchy skin.
- Spider-like blood vessels on the skin.
Causes of Cirrhosis of the Liver
The primary causes of cirrhosis include chronic alcohol abuse, hepatitis B and C infections, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and autoimmune disorders. These conditions lead to long-term liver inflammation, gradually causing scarring and irreversible damage to liver tissue.
Causes of Cirrhosis:
- Chronic alcohol abuse: One of the leading causes of cirrhosis, long-term alcohol use severely damages liver cells.
- Hepatitis B and C infections: Viral infections cause long-term liver inflammation, leading to scarring.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This condition is associated with obesity and diabetes.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions where the immune system attacks liver cells, causing cirrhosis.
Stages of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis progresses through several stages, each one representing an increasing level of liver damage. Understanding these stages is crucial for early intervention and treatment, as it can help prevent the need for a liver transplant for cirrhosis. As cirrhosis advances, the liver’s ability to perform its essential functions diminishes, leading to more severe symptoms and complications.
- Stage 1: Compensated Cirrhosis
In this initial stage, the liver is damaged but still able to perform most of its functions. There may be no noticeable symptoms, but scarring has begun. - Stage 2: Early Signs of Cirrhosis
At this stage, symptoms like mild fatigue and swelling may appear, along with complications such as portal hypertension. - Stage 3: Decompensated Cirrhosis
More severe symptoms emerge, including ascites (fluid accumulation), jaundice, and liver failure. This stage often necessitates a partial liver transplant for cirrhosis. - Stage 4: End-Stage Liver Disease
This is the most advanced stage, where the liver is unable to function. A liver transplant for cirrhosis is often the only life-saving option at this point.
Recognizing the signs of cirrhosis early and seeking timely medical intervention can significantly improve outcomes and delay progression to the later stages.
Treatment for Cirrhosis
When it comes to managing cirrhosis, early diagnosis and intervention are key to slowing its progression. Treatment for cirrhosis focuses on addressing the underlying cause, preventing further liver damage, and managing complications. In more advanced stages, a liver transplant for cirrhosis may become necessary. Here are the main approaches to treatment:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to control symptoms and manage the underlying causes. For example, antiviral drugs can treat hepatitis, while diuretics help reduce fluid buildup.
- Lifestyle changes: Patients are advised to avoid alcohol completely, as it exacerbates liver damage. A healthy, low-sodium diet can also reduce swelling and improve overall liver function.
- Monitoring and managing complications: Cirrhosis can lead to serious complications like variceal bleeding, infections, and fluid retention. Regular medical check-ups are essential to keep these risks in check.
When cirrhosis reaches an advanced stage, medical interventions may no longer be enough to maintain liver function. At this point, a partial liver transplant for cirrhosis or a full liver transplant becomes the primary treatment option, offering patients a new lease on life. This procedure replaces the damaged liver with a healthy one, restoring function and improving quality of life.
Preventing Cirrhosis
Preventing cirrhosis is key to maintaining liver health and avoiding the need for serious treatments like a liver transplant for cirrhosis. Cirrhosis develops slowly over time, but certain lifestyle choices and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of liver damage. By adopting healthy habits early, you can protect your liver and lower the chances of cirrhosis progression.
Essential steps to prevent cirrhosis:
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol use is one of the leading causes of cirrhosis. Reducing alcohol intake or quitting altogether can greatly minimize liver damage.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can lead to fatty liver disease, which increases the risk of cirrhosis. A balanced diet and regular exercise help keep your liver in good condition.
- Get vaccinated: Protect yourself against hepatitis B, a common cause of cirrhosis, by getting vaccinated.
- Avoid risky behaviors: Sharing needles or unprotected sex increases the risk of hepatitis infections that can lead to cirrhosis.
- Eat a liver-friendly diet: Focus on fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support liver health.
Taking these preventive measures can significantly lower your chances of developing liver damage and reduce the need for a liver transplant for cirrhosis later in life. Prevention is always better than treatment.
Latest Research and Advances
Recent breakthroughs in medical research are transforming the landscape of liver transplant for cirrhosis, offering new hope to patients. These advancements focus on improving the success rates of liver transplants, reducing recovery times, and exploring alternatives to traditional transplants. With cirrhosis being a leading cause of liver failure, the demand for innovative treatments is higher than ever.
Here are some key advances in liver transplant for cirrhosis:
- Regenerative Medicine: Researchers are exploring ways to stimulate liver regeneration without requiring a full transplant. This could be particularly useful in treating patients in the early stages of cirrhosis.
- Living Donor Transplants: New techniques for partial liver transplant for cirrhosis allow living donors to provide a portion of their liver, which regenerates in both the donor and recipient.
- Anti-rejection Medications: Advances in medications are reducing the risk of transplant rejection, improving long-term success rates for patients who receive a liver transplant for cirrhosis.
- 3D Bioprinting: The potential of 3D printing liver tissues is being explored, with the hope that lab-grown tissues may someday eliminate the need for donor livers.
These breakthroughs are shaping a future where liver transplant for cirrhosis will become even more effective, potentially saving more lives.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer and often occurs in individuals with cirrhosis, particularly those with Hep B cirrhosis. When liver cells become cancerous, a transplant might be the best treatment, particularly if the tumor is small and confined to the liver. Early diagnosis of HCC is critical, and a liver transplant can:
- Remove the cancerous cells and the cirrhotic liver.
- Improve long-term survival rates.
- Offer a potential cure, especially for small, localized tumors.
A liver transplant not only eliminates the tumor but also replaces the damaged liver caused by cirrhosis.
Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis, especially Hepatitis B (Hep B) and Hepatitis C, is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis. Chronic viral infections damage liver cells over time, leading to scarring and liver failure. A liver transplant is often the last resort when Hep B cirrhosis has progressed to an advanced stage. Here’s how viral hepatitis can impact the liver:
- Hepatitis B can lead to chronic infection and cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis C is another major cause of liver damage and scarring.
- Both conditions significantly increase the risk of liver cancer (HCC).
Treatment of viral hepatitis alongside a liver transplant can offer hope for patients with severe liver damage.
Conclusion
If cirrhosis has advanced to the point where it threatens your life, a liver transplant for cirrhosis could be your best chance at survival. The procedure can offer patients a new lease on life, freeing them from the debilitating symptoms of end-stage liver disease. While the process is complex, the success rate of liver transplants continues to improve with advances in medical technology. Take the first step by consulting your doctor about liver transplant for cirrhosis, and don’t wait until it’s too late.