Fatty liver disease, once a rare condition, has now become increasingly prevalent in today’s society due to lifestyle and dietary changes. In this guide, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of fatty liver disease, including its causes, symptoms, and potential risks. We’ll also explore effective prevention strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help protect your liver health. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the essential knowledge needed to take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthier liver and overall well-being.
Overview
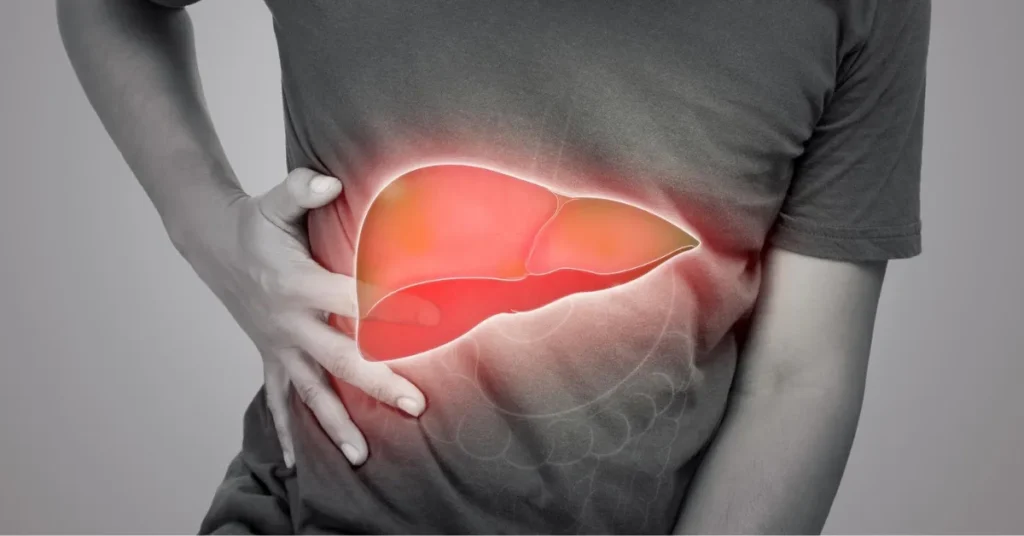
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. A small amount of fat in the liver is normal, but when fat makes up more than 5-10% of the liver’s weight, it can lead to liver damage. This condition can develop in people who drink little or no alcohol, which is referred to as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In cases where fat buildup is accompanied by inflammation or liver damage, it progresses to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH disease), a more serious form of NAFLD.
Key points to understand about fatty liver disease:
- NAFLD: Fat buildup in the liver not related to alcohol consumption.
- NASH disease: A more severe form of NAFLD that includes liver inflammation.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): Caused by excessive alcohol use.
Factors that increase the risk of fatty liver disease include obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and poor diet. Fortunately, early detection and lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and dietary adjustments, can help reverse the condition before it progresses to more severe stages, such as cirrhosis or liver failure. Taking action early is crucial in managing fatty liver disease effectively.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease often develops without obvious signs in its early stages. However, as the condition worsens, certain symptoms may arise. It’s important to pay attention to these signs, as they can indicate that the liver is struggling:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Feeling unusually tired or lacking energy throughout the day.
- Discomfort or Pain: Experiencing pain or a dull ache in the upper right side of the abdomen where the liver is located.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying, which can signal liver problems.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes in more severe cases of fatty liver disease.
- Enlarged Liver (Hepatomegaly): Noticeable swelling or enlargement of the liver, making it feel bigger than normal.
- Nausea or Feeling of Fullness: Frequently feeling nauseous or overly full, even after eating small amounts.
Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Understanding the causes of fatty liver disease can help identify who is at risk. Fatty liver occurs when your body produces too much fat or doesn’t metabolize fat efficiently enough, leading to fat storage in liver cells. Here are the main causes:
- Obesity: Excess weight is one of the leading contributors to hepatic steatosis, as fat accumulates in the liver due to increased body fat.
- Type 2 diabetes: High blood sugar levels can lead to increased fat storage in the liver, worsening the condition.
- High cholesterol and triglycerides: Elevated levels of these blood fats contribute significantly to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Poor diet: Diets high in sugars, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can overload the liver with excess fat, increasing the risk of fatty liver disease.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and increased fat accumulation in the liver.
Stages of Fatty Liver Disease
Understanding the stages of fatty liver disease is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. The condition progresses through several stages, each with distinct characteristics and potential consequences.
- Simple Fatty Liver (Steatosis): This initial stage involves the accumulation of fat in the liver without any inflammation or damage. It often goes unnoticed and may not present symptoms.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Here, fat buildup is accompanied by inflammation and liver cell injury. This stage can lead to more serious liver damage if not addressed.
- Fibrosis: At this point, chronic inflammation leads to the formation of scar tissue in the liver. While the liver can still function, the scarring indicates ongoing damage.
- Cirrhosis: The most advanced stage, where significant scarring has occurred. This can severely impair liver function and may lead to complications such as liver failure or cancer.
Recognizing these stages early is vital for effective treatment and improving outcomes for those with fatty liver disease.
Treatment for Fatty Liver Disease
Treating fatty liver disease primarily involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medications. The goal is to reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. Here are the main treatment options:
Weight Loss: Achieving a weight loss of 7-10% can significantly improve liver health by reducing fat accumulation and inflammation.
Dietary Changes: A balanced diet is crucial. Focus on:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains like brown rice and oats
- Lean proteins such as chicken, turkey, and fish
- Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil
Regular Exercise: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly helps burn fat and improve liver function.
Control Blood Sugar and Cholesterol: Managing conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol can help prevent further liver damage. Medications may be prescribed if necessary.
NAFLD Medication: While there’s no specific medication approved for fatty liver disease, some drugs are being studied to target liver fat directly and reduce inflammation.
In severe cases, especially with NASH disease, a healthcare provider may discuss advanced options like liver transplant surgery if the liver sustains significant damage. Regular monitoring and follow-ups are essential for effective management.
Prevention of Fatty Liver Disease
Preventing fatty liver disease is largely about adopting a healthy lifestyle and making informed dietary choices. Here are key strategies to help you reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a body mass index (BMI) within the normal range. Losing just 5-10% of your body weight can significantly decrease liver fat.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole foods. Incorporate:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains like brown rice and quinoa
- Lean proteins, such as fish and chicken
- Healthy fats from sources like avocados and nuts
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly. Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming can help burn fat and improve liver health.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to liver damage. If you drink, do so in moderation, and consult your doctor about your limits.
- Control Underlying Health Conditions: Effectively managing diabetes, high cholesterol, and hypertension is crucial. Regular check-ups can help monitor these conditions.
By making these lifestyle adjustments, you can significantly lower your risk of developing fatty liver disease and promote overall liver health. Prioritizing prevention is a key step toward a healthier future.
Complications of Fatty Liver Disease
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can lead to several serious complications that significantly impact overall health. Understanding these potential risks is crucial for effective management and early intervention.
- Liver Cirrhosis: Prolonged inflammation and damage from NASH disease can result in cirrhosis, a condition where healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue. This severely affects liver function and can lead to liver failure.
- Liver Cancer: Chronic inflammation and damage from fatty liver disease increase the risk of developing liver cancer. Patients with advanced hepatic steatosis are particularly vulnerable, highlighting the need for regular monitoring.
- Liver Transplant Surgery: In severe cases, where liver function is critically impaired due to cirrhosis or cancer, a liver transplant surgery may become necessary. This complex procedure requires careful evaluation and is a significant step for affected individuals.
- Cardiovascular Disease: There is a strong link between fatty liver disease and cardiovascular conditions. Individuals with liver fat accumulation often experience:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Increased risk of heart attacks or strokes
Recognizing these complications emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and proactive management of fatty liver disease.
Nonalcoholic NASH Hepatitis
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) is a more severe form of fatty liver disease that occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver and leads to inflammation and liver cell damage. Unlike simple fatty liver, which is often benign, NASH can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer if not addressed. NASH is part of a spectrum of conditions under nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and it is commonly associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
Key aspects of NASH Hepatitis:
- Liver Inflammation: Chronic inflammation caused by fat accumulation leads to liver damage.
- Fibrosis Progression: NASH can result in scarring, or fibrosis, which impairs liver function.
- Associated Conditions: Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and high cholesterol are common factors that contribute to NASH development.
- Silent Symptoms: Many patients with NASH hepatitis remain asymptomatic for years, making it difficult to detect without proper screening.
- Lifestyle Impact: Diet, exercise, and weight management are crucial in preventing and treating NASH.
Timely diagnosis and treatment are vital for managing NASH hepatitis, reducing the risk of severe liver damage, and preventing progression to cirrhosis or liver failure.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a growing health concern worldwide, but it’s preventable and manageable with the right steps. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and stages of this condition, you can take action early and avoid its progression. Lifestyle changes such as improving your diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol are key to keeping your liver healthy. If you’re concerned about fatty liver disease, consult your healthcare provider to discuss potential treatments and next steps.