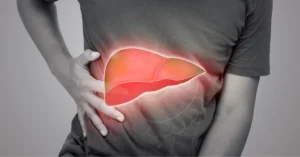
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, once a rare condition, has now become

Liver transplant surgery is a life-saving procedure performed to replace a diseased or failing liver with a healthy one from a donor. It is typically reserved for patients who have reached the end-stage of liver disease and for whom all other treatment options have been exhausted. The process is complex and involves careful coordination between medical teams, the patient, and the donor.
Here are the key points to understand about liver transplant surgery:
Understanding these aspects of liver transplant surgery helps patients and their families prepare for what to expect and underscores the importance of thorough medical care and ongoing support.
Cirrhosis is one of the primary reasons for liver transplant surgery. It involves the severe scarring of liver tissue, which progressively impairs the liver's ability to function effectively. When cirrhosis advances to the point where the liver fails, a liver transplant becomes the most viable option to save the patient’s life. This section delves into the importance of liver transplant surgery for cirrhosis and highlights critical points to understand about this condition.
Understanding the critical role of liver transplant surgery for cirrhosis is vital for patients and their families. Early diagnosis, regular monitoring, and timely intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes, offering hope and a better quality of life.
Liver transplant surgery is a critical intervention for patients with severe liver conditions that can no longer be managed by other treatments. The reasons for requiring a liver transplant are diverse, reflecting the various ways in which the liver can become damaged and cease to function effectively. Here are some of the primary reasons why a liver transplant may be necessary:
Each of these conditions highlights the critical need for liver transplant surgery as a lifesaving measure. Understanding these reasons can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment options and timing.
Acute liver failure is a sudden and severe decline in liver function, often occurring within days or weeks. Unlike chronic liver conditions that develop over years, acute liver failure can quickly become life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention. This rapid onset condition can be caused by various factors, and understanding these can help in recognizing the symptoms early and seeking timely treatment.
Causes of Acute Liver Failure:
Immediate medical intervention is crucial in cases of acute liver failure. Treatment often involves hospitalization, supportive care, and in many instances, liver transplant surgery. Early recognition and prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes and save lives.
Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a significant indication for liver transplant surgery. When the cancer is localized to the liver and has not spread to other parts of the body, a liver transplant can be a potential cure. The surgery involves replacing the cancerous liver with a healthy one from a donor, offering patients a chance for a cancer-free life.
HCC often develops in the setting of chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis, and its treatment can be complex. Here are some crucial points to understand about liver cancer as an indication for liver transplant surgery:
In conclusion, liver transplant surgery offers a beacon of hope for liver cancer patients, particularly those diagnosed early and meeting the criteria for transplantation. This life-saving procedure underscores the importance of regular screening and early intervention in managing liver cancer.
Metabolic liver diseases are a group of inherited conditions that disrupt the normal metabolic processes in the liver. These disorders can lead to severe liver damage, and in many cases, liver transplant surgery is required to restore liver function and improve the patient’s quality of life.
One of the most well-known metabolic liver diseases is Wilson’s disease, which causes an excessive accumulation of copper in the liver. Similarly, hemochromatosis leads to iron overload in the liver, resulting in significant damage over time. Both conditions are genetic and require lifelong management.
For patients with these diseases, a liver transplant can provide a cure by replacing the damaged liver with a healthy one. Here are some key points about metabolic liver diseases and their implications:
Managing metabolic liver diseases involves regular monitoring, medication to control metal levels, and in severe cases, considering liver transplant surgery. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with these conditions.
Severe liver damage or failure, often due to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, or acute liver failure, indicates the need for a liver transplant when other treatments are ineffective.
In India, the most common indication for a liver transplant is cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or C infection, followed by alcoholic liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Globally, cirrhosis, particularly due to chronic hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease, is the most common reason for requiring a liver transplant.

Fatty liver disease, once a rare condition, has now become
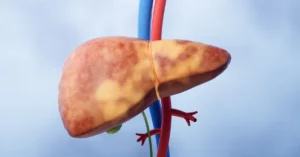
Cirrhosis of the liver is a serious medical condition that

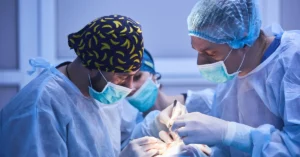
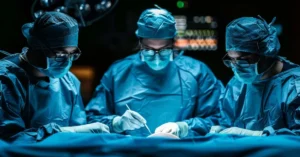

Undergoing a liver transplant is a monumental step in treating
A liver transplant is a crucial and intricate surgical procedure
Embarking on a liver transplant journey in India is a
Hepatitis B and C are two of the most common and serious viral infections affecting the liver. They can lead to chronic liver disease, liver cancer, and even necessitate a liver transplant. This blog post will explore hepatitis B and C in detail, covering their symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention methods.

The donor matching process is a critical component of liver transplantation, where a liver transplant donor offers a life-saving opportunity to those suffering from severe liver conditions. Matching a donor with a recipient involves a detailed and complex series of steps, each designed to ensure that the donated liver provides the best possible outcome.
Liver transplant is a life-saving procedure for individuals suffering from severe liver diseases. This complex surgery involves replacing a diseased liver with a healthy one from a donor. The journey towards a liver transplant can be daunting, but understanding the process, benefits, and risks can help patients make informed decisions.

Undergoing a liver transplant is a monumental step in treating severe liver disease, but the journey to recovery continues well beyond the operating room. Post-surgical care is crucial for ensuring the success of the liver transplant and improving the patient’s overall health.