Liver cancer is a serious and life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people worldwide. With early detection and proper treatment, there is hope for managing and even overcoming this disease. We will delve into the complexities of liver cancer, exploring its definition, types, symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention methods. By understanding liver cancer, we can better navigate this challenging diagnosis and take proactive steps toward health.
Definition
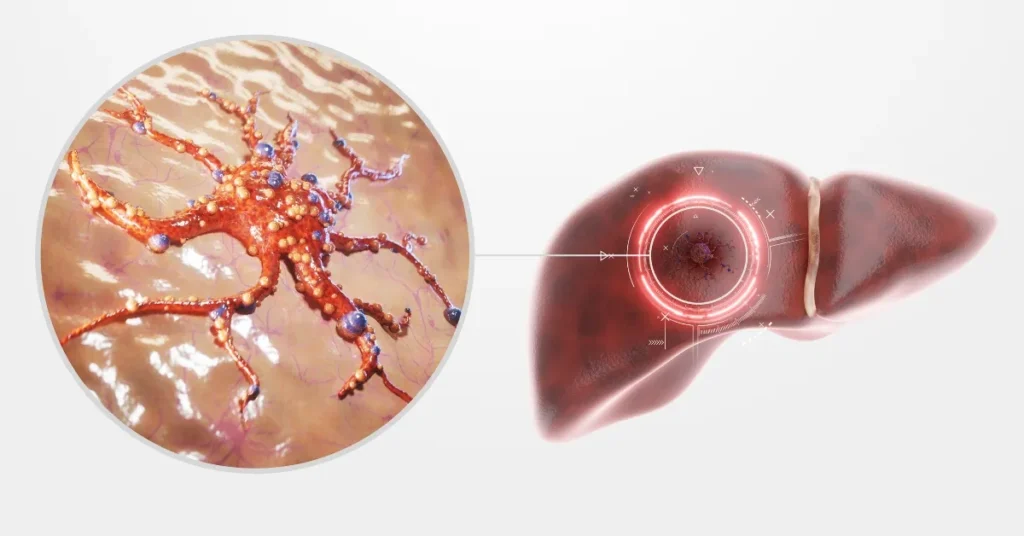
Liver cancer, a life-threatening condition, occurs when abnormal cells in the liver grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors. These tumors interfere with the liver’s essential functions, such as detoxifying the blood, producing bile, and storing nutrients. Understanding the definition of liver cancer is crucial for recognizing the severity and implications of this disease.
- Malignant Tumors: Liver cancer is characterized by the development of malignant tumors within the liver. These tumors can either originate in the liver (primary liver cancer) or spread to the liver from other parts of the body (secondary or metastatic liver cancer).
- Types of Liver Cancer: The most common type is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which starts in the main liver cells called hepatocytes. Other types include intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer), angiosarcoma, hemangiosarcoma, and hepatoblastoma, which primarily affects children.
- Impact on Liver Function: Malignant tumors in the liver disrupt its ability to perform vital functions, leading to symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, and weight loss. The liver’s role in detoxifying the body and metabolizing nutrients becomes compromised.
- Chronic Liver Disease Link: Liver cancer often develops in individuals with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. These conditions cause long-term liver damage, increasing the risk of cancer.
- Diagnosis and Prognosis: Early detection of liver cancer significantly improves the prognosis. Regular screenings and awareness of risk factors can lead to early diagnosis, enabling more effective treatment options.
By comprehensively understanding the definition of liver cancer, patients and caregivers can better grasp the importance of early detection and the impact of this disease on overall health.
Types of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer, a serious condition affecting many people worldwide, can be categorized into several types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. Understanding these types is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
- Stage 1: The cancer is confined to the liver, with a single tumor that hasn’t invaded blood vessels. This stage is often asymptomatic and has the best prognosis with potential curative treatments like surgical resection or ablation.
- Stage 2: Multiple small tumors or a single tumor that has invaded blood vessels. Treatment may include surgery, liver transplant, or localized therapies.
- Stage 3: Multiple tumors larger than 5 cm, or tumors invading a major vein. Treatment options are more limited and may involve a combination of therapies.
- Stage 4 Liver Cancer: The cancer has spread beyond the liver to other parts of the body. Treatment focuses on prolonging life and palliating symptoms, often involving systemic therapies and palliative care.
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
- Originates in the bile ducts within the liver and can cause bile duct blockages, leading to jaundice. Treatment includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Angiosarcoma and Hemangiosarcoma
- Rare cancers originating in the blood vessels of the liver. They are typically aggressive and difficult to treat, often requiring a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
Hepatoblastoma
- A rare liver cancer primarily affecting children under the age of 3. Early diagnosis and treatment, including surgery and chemotherapy, can lead to a good prognosis.
Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A rare subtype of HCC that typically affects younger individuals without a history of liver disease. Surgical resection is the primary treatment, and it generally has a better prognosis compared to traditional HCC.
Each type of liver cancer presents unique challenges and requires specific treatment strategies. Consulting with a liver oncologist is essential to determine the most effective approach based on the cancer type and stage.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Symptoms of liver cancer include unexplained weight loss, persistent abdominal pain, swelling, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. These symptoms often appear in advanced stages, making early detection challenging.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden and significant weight loss without trying is a common symptom of liver cancer.
- Loss of Appetite: A noticeable reduction in appetite can indicate liver issues.
- Upper Abdominal Pain: Persistent pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen is a key symptom.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Frequent feelings of nausea and episodes of vomiting may occur.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice, indicates liver dysfunction.
Causes of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer arises from various underlying factors that damage the liver over time. Understanding these causes is crucial in taking preventive measures and seeking early treatment. Here are the primary causes of liver cancer:
- Chronic Hepatitis B and C Infections: Long-term infection with hepatitis B or C viruses can lead to liver cancer. These viruses cause chronic inflammation and damage to liver cells, which can eventually lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Regular screening and antiviral treatments can help manage these infections.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis, which is severe scarring of the liver tissue, is a major risk factor for liver cancer. It can result from chronic hepatitis infections, long-term alcohol abuse, or other liver diseases. Cirrhosis disrupts normal liver function and creates a favorable environment for cancerous growths to develop.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD is increasingly recognized as a cause of liver cancer. This condition, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver in individuals who consume little to no alcohol, can progress to cirrhosis and increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Genetic Disorders: Certain inherited conditions, such as hemochromatosis, which causes excessive iron accumulation in the liver, and Wilson’s disease, which leads to copper buildup, can increase the risk of developing liver cancer. Early diagnosis and management of these conditions are essential.
- Exposure to Aflatoxins: Aflatoxins are toxic substances produced by molds that grow on poorly stored crops like grains and nuts. Long-term exposure to aflatoxins is a significant risk factor for liver cancer, particularly in regions with inadequate food storage facilities.
Treatment for Liver Cancer
Treating liver cancer effectively depends on the stage and type of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Early diagnosis can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. Here are some of the primary treatments for liver cancer, including options for stage 4 liver cancer treatment:
Surgical Resection
- This involves surgically removing the portion of the liver that contains the cancerous tumors. It is most effective for early-stage liver cancer and can lead to long-term survival if the cancer has not spread.
Liver Transplant
- A liver transplant involves replacing the diseased liver with a healthy donor liver. This option is particularly beneficial for patients with small, localized tumors and cirrhosis. Patients must meet specific criteria for transplant eligibility, including the size and number of tumors and overall health.
Ablation Therapies
- These treatments destroy cancer cells without removing them. Methods include radiofrequency ablation, which uses heat, and cryoablation, which uses extreme cold. Ablation is often used for patients who are not candidates for surgery.
Embolization Therapies
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radioembolization involve blocking the blood supply to the tumor, delivering chemotherapy or radioactive particles directly to the cancer cells. These therapies are often used for intermediate-stage liver cancer.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
- These advanced treatments focus on specific pathways that cancer cells use to grow. Targeted therapy drugs, such as sorafenib, and immunotherapy, which boosts the body’s immune response against cancer, offer hope for patients with advanced liver cancer, including stage 4 liver cancer treatment.
Each of these treatment options has its own benefits and risks, and a liver oncologist can help determine the best approach based on individual patient factors.
Stage 4 Liver Cancer Treatment
Stage 4 liver cancer, also known as advanced liver cancer, indicates that the cancer has spread beyond the liver to other parts of the body. This stage is challenging to treat and cure, but several treatment options aim to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Consulting with a liver oncologist is crucial for developing a personalized treatment plan. Here are some of the primary treatment options for stage 4 liver cancer:
- Systemic Chemotherapy: Uses powerful drugs to target and kill cancer cells throughout the body. While it may not cure stage 4 liver cancer, chemotherapy can help shrink tumors and alleviate symptoms.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. Drugs like sorafenib (Nexavar) can inhibit tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis, slowing the progression of stage 4 liver cancer.
- Immunotherapy: Enhances the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. Drugs such as nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) have shown promise in treating advanced liver cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. This treatment can help control pain and other symptoms caused by tumors in the liver or other affected areas.
- Palliative Care: Focuses on relieving symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients with stage 4 liver cancer. This may include pain management, nutritional support, and psychological counseling.
These treatments aim to extend life expectancy and enhance the quality of life for those battling stage 4 liver cancer.
Prevention of Liver Cancer
Preventing liver cancer is crucial for reducing the incidence and improving overall health outcomes. By taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing this life-threatening condition. Here are essential strategies for liver cancer prevention:
Get Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
- The hepatitis B virus is a major cause of liver cancer. Vaccination is a powerful tool in preventing infection and subsequently lowering liver cancer risk.
Regular Screening for High-Risk Individuals
- Those with chronic hepatitis B or C infections, cirrhosis, or a family history of liver cancer should undergo regular liver screening. Early detection through imaging tests and blood tests can catch liver cancer at a treatable stage.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking can lead to liver cirrhosis, a precursor to liver cancer. A balanced diet and regular exercise can prevent obesity and diabetes, both risk factors for liver cancer.
Avoid Exposure to Aflatoxins
- Aflatoxins, found in improperly stored grains and nuts, are potent carcinogens. Ensuring food is stored correctly and consuming only fresh, uncontaminated products can reduce exposure to these toxins.
Treat Underlying Liver Conditions
- Managing chronic liver diseases like hepatitis B and C with antiviral medications can prevent liver damage and decrease the risk of liver cancer. Regular medical follow-up and adherence to treatment plans are essential.
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of liver cancer and promote overall liver health.
Conclusion
Liver cancer is a daunting diagnosis, but with advancements in medical treatments and a proactive approach to prevention, there is hope. Liver oncologists play a crucial role in guiding patients through their treatment journey, from early-stage interventions to stage 4 liver cancer treatment. Understanding liver cancer, its causes, and treatment options empowers patients and families to make informed decisions and take steps toward a healthier future.