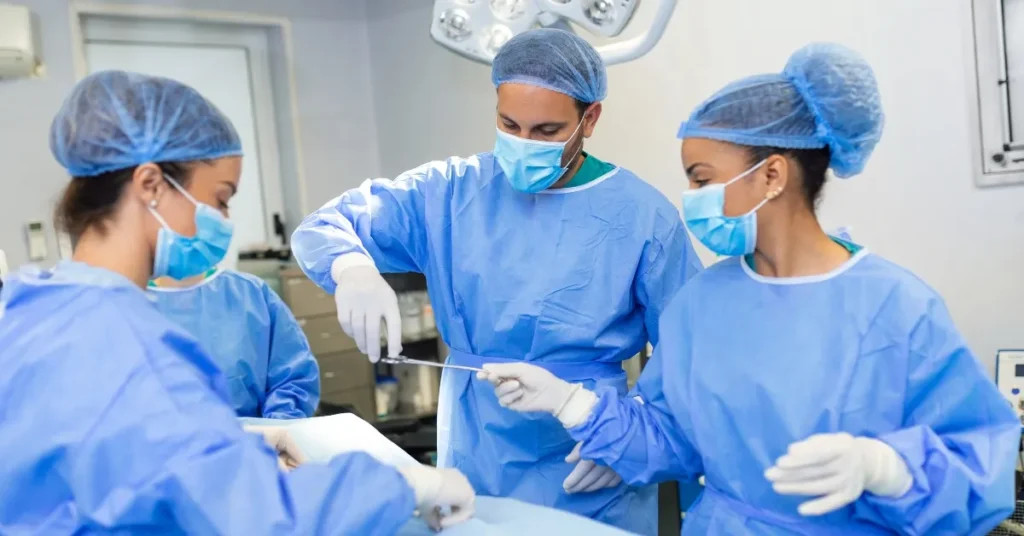
The liver transplant process is a critical procedure for individuals with end-stage liver disease, offering them a new lease on life. This complex surgery involves replacing a diseased liver with a healthy one from a donor. The liver transplant process includes multiple stages, from donor selection to the actual surgery and recovery. Understanding each step of the liver transplant process can help patients and their families prepare for what’s ahead, making the journey less daunting and more manageable.
Donor Liver Procurement
The first step in the liver transplant process is securing a healthy liver from a donor. This crucial step can involve either a deceased or living donor, depending on the circumstances and the availability of organs. In most cases, a donor liver comes from someone who has passed away and agreed to donate their organs. However, some patients receive part of a liver from a living donor, such as a relative or friend, as the liver is one of the few organs that can regenerate itself.
Key points about donor liver procurement:
- Deceased donor: In this case, the liver is taken from an individual who has been declared brain-dead but whose organs are still functioning. This donor would have previously registered for organ donation.
- Living donor: A part of the liver can be donated by a living individual, usually a close family member, due to the liver’s unique ability to regenerate.
- Organ matching: The donor liver must match the recipient’s blood type and body size to minimize rejection risk.
Once the donor liver is secured, it is quickly transported to the hospital for the transplant surgery. Proper timing is essential, as the liver transplant process depends on the liver being viable and in good condition.
Recipient Preparation
The liver transplant process begins well before the actual surgery, with careful preparation of the recipient to ensure the procedure’s success. This stage involves comprehensive medical evaluations to confirm that the patient is fit for the transplant and can handle the demands of such a major surgery. During this phase, doctors assess the recipient’s overall health and determine their suitability for the transplant.
Liver transplant in India typically involves:
- Medical Tests: Blood tests, imaging studies (CT scans, MRIs), and heart and lung function tests are conducted to ensure the recipient is physically ready for the surgery.
- Matching the Donor: Doctors match the recipient with a donor liver based on factors like blood type and body size to reduce the risk of organ rejection.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Medications to suppress the immune system are often started in advance to prepare the body for the organ transplant process.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Recipients may be asked to stop smoking, adjust their diet, or start exercising to improve their overall health.
This preparation is crucial in minimizing potential complications during and after the surgery. Proper recipient preparation can significantly impact the liver transplant surgery time and ensure a smoother recovery process post-operation.
Anesthesia and Incision
The liver transplant process involves several critical stages, one of which is the administration of anesthesia and making the incision. Before the liver transplant surgery begins, the patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure they remain unconscious and pain-free throughout the operation. The anesthesia process is carefully managed by a skilled anesthesiologist, who monitors the patient’s vital signs and adjusts medications to keep the patient stable.
Once the patient is under anesthesia, the surgeon makes a large incision in the abdomen to access the liver. This step is essential for the successful completion of the liver transplant process. The incision typically extends across the upper abdomen, just below the ribcage.
- General anesthesia ensures the patient feels no pain during the surgery.
- The incision provides access to the liver, which is located beneath the diaphragm.
- The size and location of the incision allow the surgeon to see the liver clearly and work with precision.
This part of the liver transplant in India is crucial because it sets the stage for the removal of the diseased liver and implantation of the donor liver. The precise placement of the incision ensures minimal complications and facilitates a smoother recovery after the surgery.
Hepatectomy
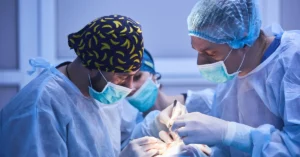
Hepatectomy is a crucial step in the liver transplant process, where the diseased liver is carefully removed to make space for the donor liver. This part of the surgery requires precision and skill as the liver is a vital organ, connected to major blood vessels and the bile ducts. The process of removing the liver is intricate, and surgeons must work meticulously to ensure no damage is done to the surrounding organs or tissues.
During hepatectomy, several important steps take place:
- Clamping of blood vessels: Surgeons temporarily stop blood flow to and from the liver by clamping the major blood vessels. This prevents excessive bleeding during the procedure.
- Disconnection of bile ducts: The bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the intestine, are carefully disconnected to allow the removal of the liver.
- Separation of the liver from surrounding tissues: The liver is gently detached from its surrounding structures, taking care not to harm other vital organs.
Once the damaged liver is completely removed, the liver transplant surgery time proceeds to the next stage, where the new liver is implanted. Hepatectomy is a significant part of the overall organ transplant process, ensuring that the patient is ready to receive the healthy donor liver.
Implantation of Donor Liver
The implantation of the donor liver is one of the most critical steps in the liver transplant process. Once the diseased liver is removed, the surgeon carefully places the healthy donor liver into the recipient’s body. This phase involves meticulous precision, ensuring that the new liver is positioned correctly for optimal function.
During the liver transplant surgery time, which can range from 6 to 12 hours, the following steps are carried out during the implantation process:
- Positioning the liver: The donor liver is placed in the same location as the removed liver, ensuring it aligns with the body’s structures.
- Assessing the fit: The surgeon evaluates whether the liver fits well within the abdominal cavity. Any size discrepancies are addressed to ensure proper function.
- Correcting any abnormalities: If there are any minor issues with the donor liver’s shape or size, the surgeon will adjust accordingly.
Once the liver is securely in place, the surgeon begins reconnecting the blood vessels and bile ducts. This step is crucial to ensure the liver functions properly once blood flow is restored.
The liver transplant process doesn’t end with the implantation; careful monitoring is required throughout the procedure to ensure that the body accepts the new liver.
Vascular Anastomosis
One of the most intricate parts of the liver transplant process is the vascular anastomosis, where the surgeon connects the blood vessels of the new liver to the recipient’s body. This stage is critical because it ensures that the donor liver can receive oxygen-rich blood and function properly in the patient. Proper blood flow is essential for the survival and success of the new liver after the liver transplant surgery.
In this step of the liver transplant process:
- The surgeon attaches the hepatic artery from the donor liver to the recipient’s artery, allowing blood to flow to the new liver.
- The portal vein, another vital vessel, is also connected, enabling nutrient-rich blood from the intestines to reach the liver.
- Blood flow is carefully monitored to ensure there are no blockages or leaks.
These precise connections between the blood vessels ensure that the liver gets the oxygen and nutrients it needs to start working immediately after the organ transplant process.
The success of the vascular anastomosis is crucial in determining the overall outcome of the liver transplant in India. A well-executed connection allows the donor liver to function optimally, giving patients a new chance at life after the liver transplant surgery.
Bile Duct Reconstruction
Bile duct reconstruction is a crucial phase in the liver transplant process, ensuring the new liver functions properly by allowing bile to flow from the liver to the intestines. Bile is essential for digesting fats, and without proper bile flow, the digestive system would face significant complications. During this step, the surgeon reconnects the bile ducts from the donor liver to those of the recipient. This process ensures that bile can be transported effectively, promoting healthy digestion and liver function.
Key steps involved in bile duct reconstruction:
- The surgeon identifies and prepares the bile ducts from both the donor liver and the recipient.
- Careful reconnection of these ducts is done to ensure a smooth flow of bile.
- Surgeons often use fine sutures to reconnect the ducts to prevent any leakage or obstruction.
- A bile duct stent may be inserted to keep the ducts open and promote healing.
This meticulous step in the liver transplant process is vital for preventing bile leakage, which could lead to infections or other complications. A successful bile duct reconstruction significantly impacts the long-term success of the transplant, ensuring the new liver can function optimally and the recipient can recover smoothly after the liver transplant surgery.
What to Expect During Liver Transplant Surgery
Liver transplant surgery is a meticulously planned procedure that typically takes between 6 to 12 hours, depending on the complexity of the case. The liver transplant steps begin with anesthesia, followed by the removal of the diseased liver. Once the liver is removed, the surgeon will either implant a healthy liver from a deceased donor or a portion of a living donor’s liver. The new liver is then connected to the patient’s blood vessels and bile ducts, ensuring it functions properly. Throughout the surgery, a highly skilled medical team will monitor vital signs and manage any potential complications.
Patients undergoing a liver transplant can expect personalized care from experienced transplant teams in Chennai’s multispeciality hospitals, where every step of the procedure is carried out with precision to ensure the highest chances of success.
What to Expect After a Liver Transplant
The recovery process after a liver transplant is just as crucial as the surgery itself. Immediately after the transplant, patients are monitored closely in the intensive care unit (ICU) to ensure the new liver is functioning correctly. The first few days are critical, as doctors check for signs of infection, bleeding, or organ rejection. Patients can expect to stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 weeks before being discharged.
After leaving the hospital, patients will need regular check-ups, blood tests, and medication to prevent organ rejection. The recovery period can take several months, during which the transplanted liver gradually adjusts and begins to function normally. Multispeciality hospitals in Chennai provide a dedicated post-transplant care team to help patients through this recovery phase.
Conclusion
Liver transplants are complex but life-saving procedures, and multispeciality hospitals in Chennai offer the best possible care, from pre-surgery preparation to post-operative recovery. The well-coordinated liver transplant steps ensure that patients receive top-tier medical treatment, allowing for a smoother recovery and better long-term outcomes. With the expert guidance of transplant teams, patients can expect comprehensive support every step of the way.